Beyond the Divide: How Full-Stack Development Builds Better Products, Faster
It's more than just knowing a little frontend and a little backend. Discover how the full-stack mindset creates seamless, efficient, and robust digital experiences from click to cloud.
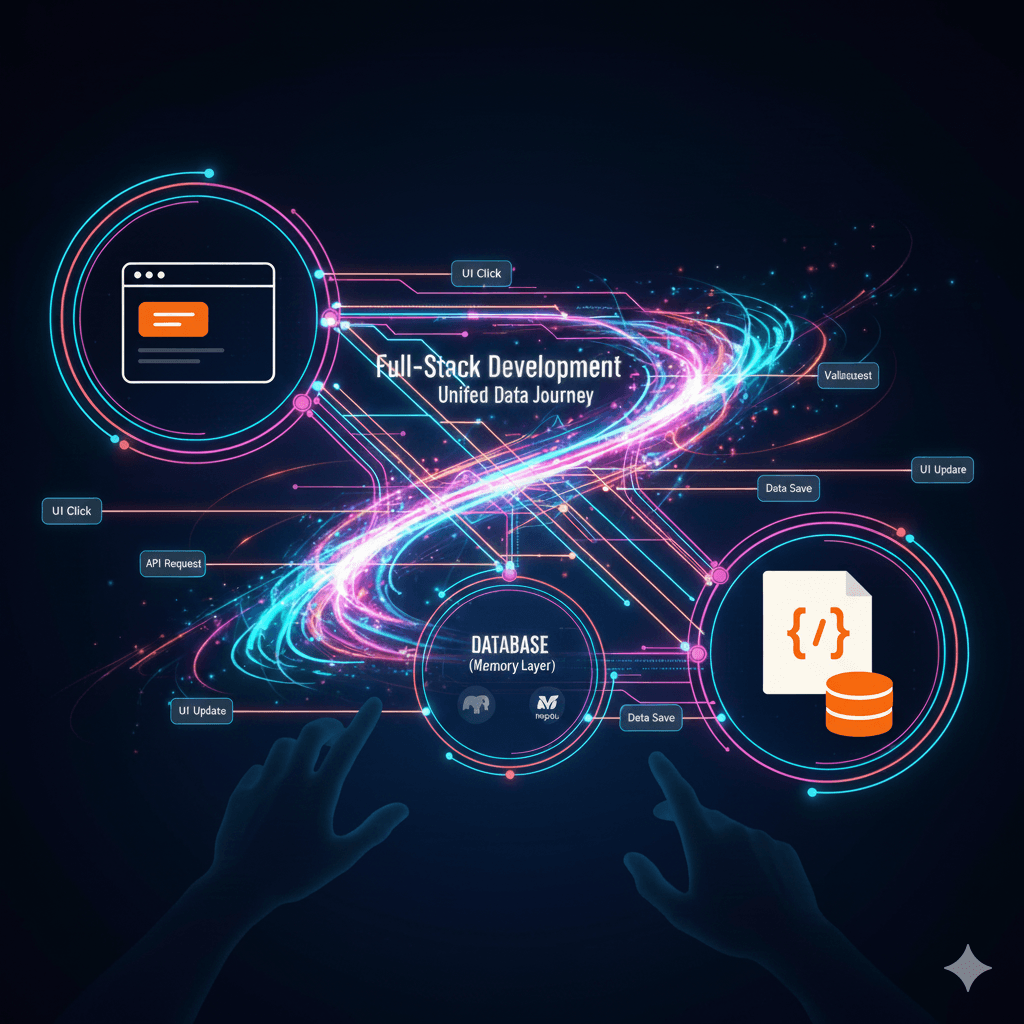
In many organizations, there's a wall between the frontend and the backend. Frontend developers build what the user sees, and backend developers build the engine that makes it run. When they meet in the middle, they communicate through a narrow window called an API. This can lead to friction, misunderstandings, and bugs that live in the gaps between the two worlds.
Full-stack development is the philosophy of tearing down that wall. It's about understanding the entire application lifecycle—from the user's click in a browser to the data being saved in a database, and all the way back again. This holistic view allows for the creation of truly cohesive, efficient, and data-driven digital ecosystems.
Let's break down how this works by tracing the journey of a single piece of data through a modern web application.
The Anatomy of a Modern Application
A full-stack application can be thought of as having three core layers, each with its own set of tools:
The Front-End (The Experience Layer): This is everything the user sees and interacts with. It's the buttons, the forms, and the layouts. The goal here is to create an intuitive, responsive, and accessible user interface (UI).
Key Technologies: React, Next.js, Vue, TailwindCSS.
The Back-End (The Logic Layer): This is the brain of the operation. It handles business logic, secures data, manages user authentication, and communicates with other services. It exposes this logic to the front-end via an API (Application Programming Interface).
Key Technologies: Node.js, Express, Python (Django/FastAPI), Go.
The Database (The Memory Layer): This is where all the application's data is stored, organized, and retrieved. It's the single source of truth for everything from user profiles to product inventory.
Key Technologies: PostgreSQL, MongoDB, MySQL, Redis.
The magic of full-stack development lies in understanding how to seamlessly connect these layers.
From Click to Database: A Full-Stack Example in Action
Imagine a simple feature: a "Like" button on a blog post. When a user clicks it, the like count should increase. Here's how that simple action travels through the fullstack, using a common Next.js + Node.js + PostgreSQL stack.
Step 1: The Front-End (React Component)
The user interacts with a React component. We use state to manage the like count and a click handler to trigger a request to our back-end API.
Code Example: LikeButton.jsx (React Front-End)
<></>
Step 2: The Back-End (Next.js API Route)
The fetch request is received by our back-end, which in Next.js can be a simple API route file. This server-side code handles the logic: it receives the postId, validates it, updates the database, and sends a response back.
Code Example: <></>
Why This Unified Approach Matters
Viewing the application as a whole, rather than as separate parts, provides huge advantages:
Efficiency and Speed:
A single developer or a tightly-knit team can design a feature from end to end, reducing communication overhead and development time.
Better Problem-Solving:
When a bug occurs, a full-stack developer can trace the problem from the UI down to the database query, leading to faster and more effective debugging.
Cohesive Architecture:** Data structures, design patterns, and logic are consistent across the entire application, making it more robust and easier to maintain.
The result is a unified digital experience that’s not only fast, secure, and future-ready but also built with a deeper understanding of how every part contributes to the whole.
Learn More:
Explore the Next.js framework for building full-stack web applications.
Learn about Prima, a next-generation ORM for Node.js and TypeScript.